Java Spring JDBC
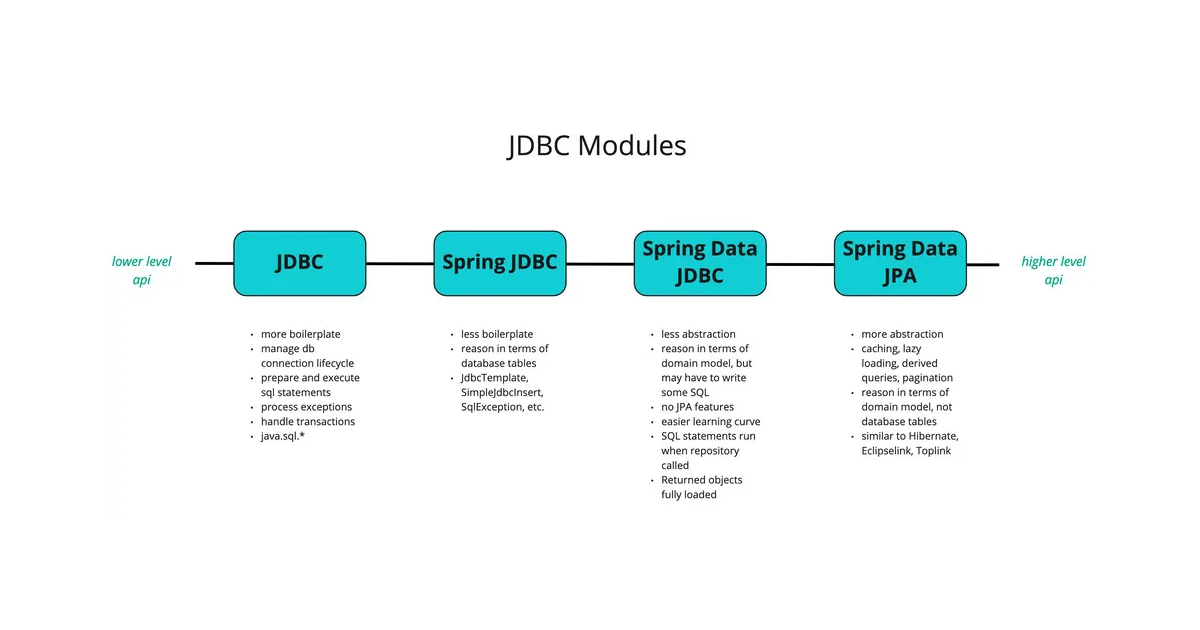
This article explains the roles and use cases of spring-session-jdbc, spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc, and spring-boot-starter-jdbc in a Spring Boot project.
1️⃣ org.springframework.session:spring-session-jdbc
✅ Features:
• A library that enables storing Spring Sessions using JDBC.
• By default, it stores session data in a database (DB), allowing session persistence even after server restarts.
✅ Use Cases:
• When sharing sessions across multiple servers in a distributed environment
• When database-based session storage is needed instead of Spring Boot's built-in session store (default In-Memory)
✅ Example Configuration (application.yml)
spring:
session:
store-type: jdbc # Use JDBC-based session storage
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
username: user
password: pass📌 Usage Example
Used when storing HTTP sessions in a DB to share sessions across multiple instances in a session management service.
@Controller
public class SessionController {
@GetMapping("/session")
public String getSession(HttpSession session) {
2️⃣ org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc
✅ Features:
• Simplifies database access using Spring Data JDBC
• Unlike Spring Data JPA, it is optimized for simple CRUD operations based on JDBC
• Useful for creating a lightweight data access layer compared to JPA
✅ Use Cases:
• When using JDBC lightly without JPA (Hibernate)
• When Repository pattern-based data access is needed without complex entity mapping
✅ Example (Repository Pattern)
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<User, Long> {
List<User> findByUsername(📌 Usage Example
Useful for simple CRUD processing using JDBC instead of JPA.
@Service
public class UserService {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public UserService(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate)
3️⃣ org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc
✅ Features:
• Provides basic configuration for JDBC-based database connection and SQL execution
• Includes DataSource, JdbcTemplate, etc., enabling direct SQL execution
• Allows lower-level JDBC usage compared to spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc
✅ Use Cases:
• When directly using JDBC in Spring Boot
• When executing SQL directly using JdbcTemplate
• When SQL needs to be executed directly without ORM (JPA)
✅ Example (Using JdbcTemplate)
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void insertUser(String username) {
jdbcTemplate.update("INSERT INTO users (username) VALUES (?)", username)📌 Usage Example
• When SQL needs to be executed directly without ORM
• When fast SQL execution is required (optimization needed for JOIN, GROUP BY, etc.)
📌 Summary
| Library | Role | When to Use? |
|---|---|---|
| spring-session-jdbc | Store sessions in DB | When session persistence and sharing across servers |
| spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc | Spring Data JDBC support | When using simple Repository pattern without JPA |
| spring-boot-starter-jdbc | Basic JDBC support | When executing SQL directly (using JdbcTemplate) |
🚀 Which one should you use?
• Basic JDBC usage in Spring Boot → spring-boot-starter-jdbc
• Simple CRUD with Repository pattern → spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc
• Session sharing & persistence across servers → spring-session-jdbc
📢 Conclusion
• spring-boot-starter-jdbc is a library for basic JDBC support.
• spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc makes it easy to apply Spring Data JDBC-based Repository patterns.
• spring-session-jdbc is used for storing and managing session data in a database.
Choose the appropriate library based on your project's requirements! 😊